01 A Tour of Computer Systems
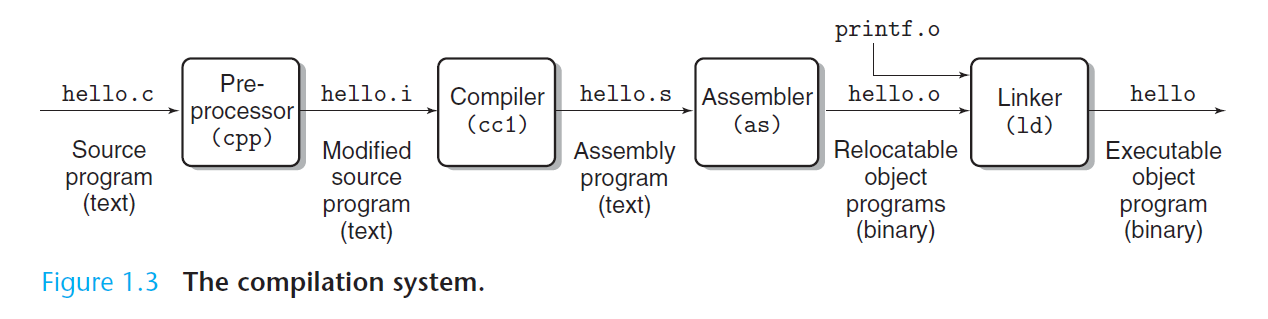
计算机是由硬件和软件组成的,它们共同协作运行应用程序。计算机内部的信息被标识为一组组的位,它们根据上下文有不同的解释方式。程序被其他程序翻译成不同的形式,开始时是 ASCII 文本,然后被编译器和连接器翻译成二进制可执行文件。
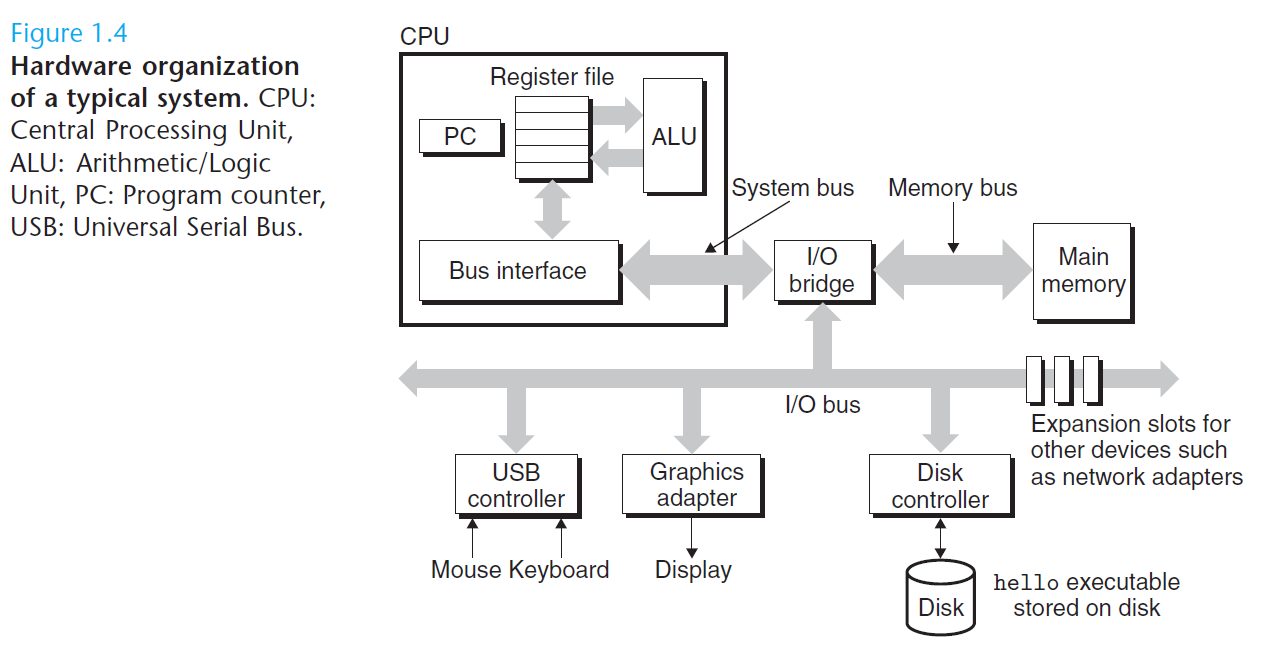
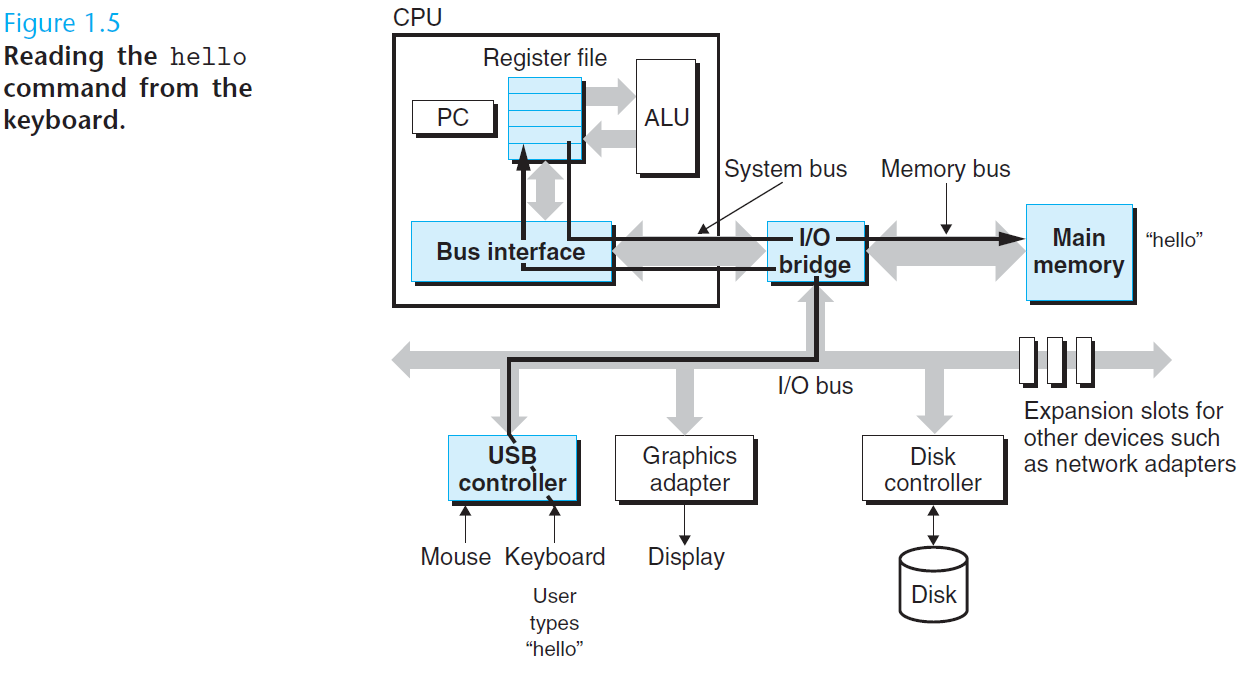
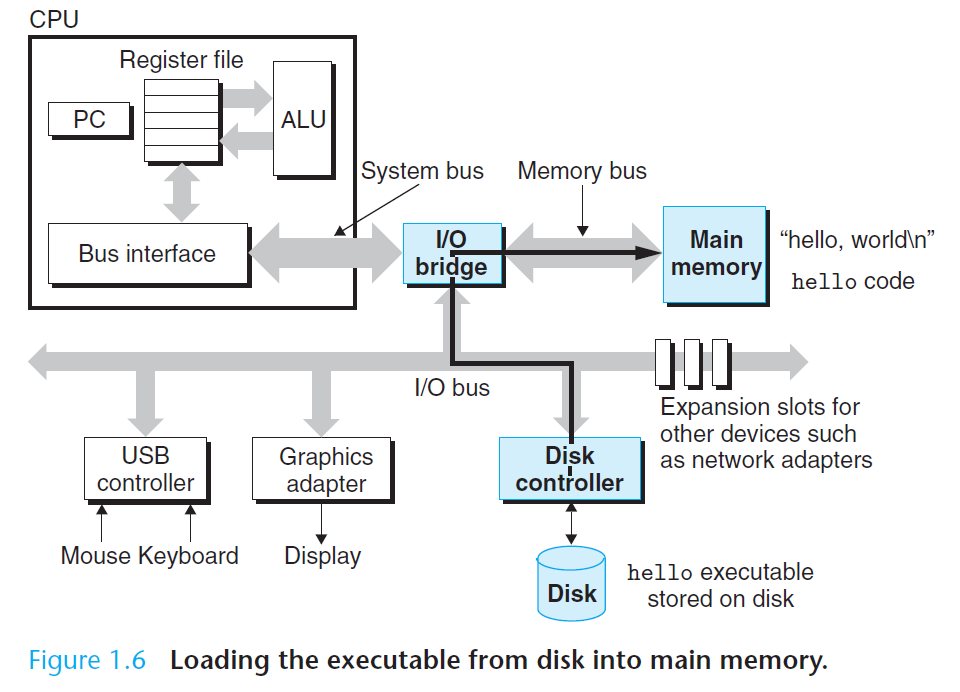
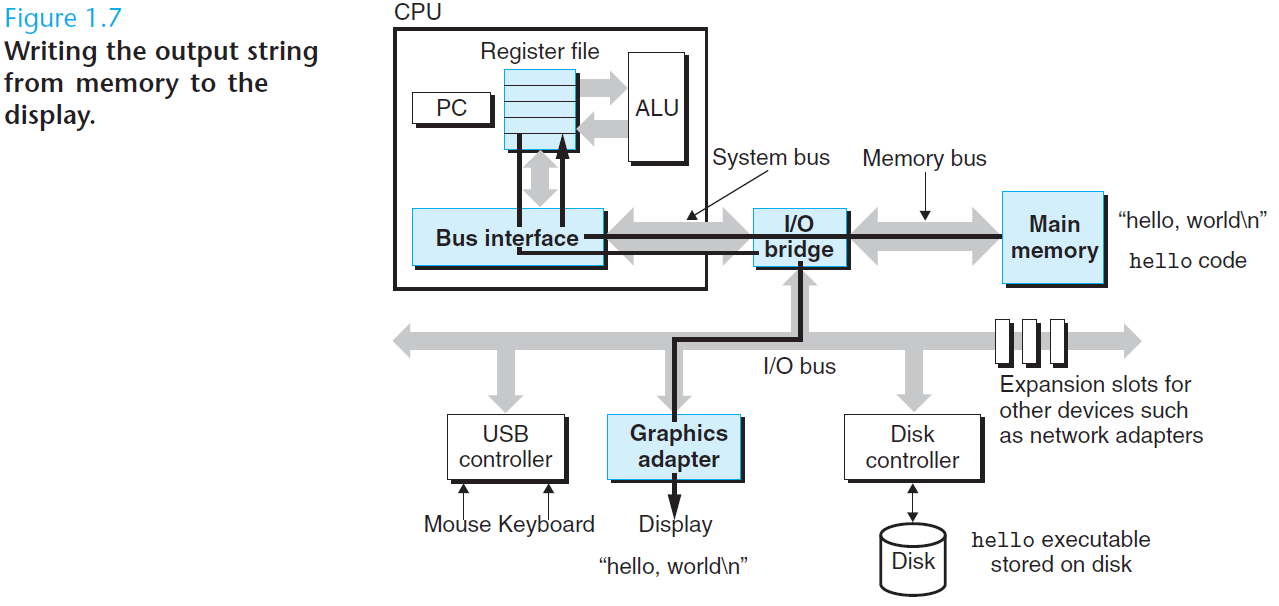
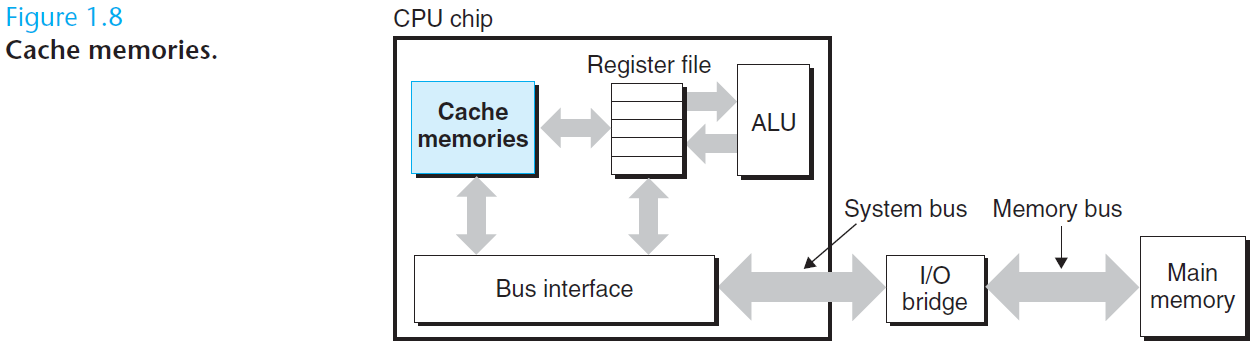
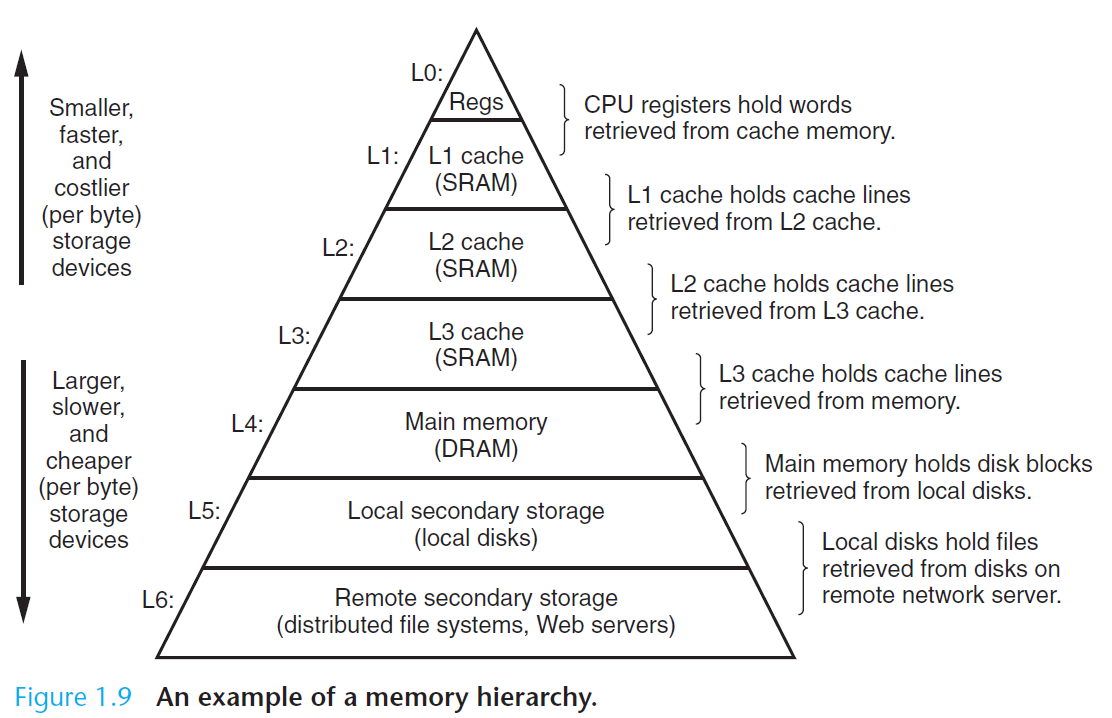
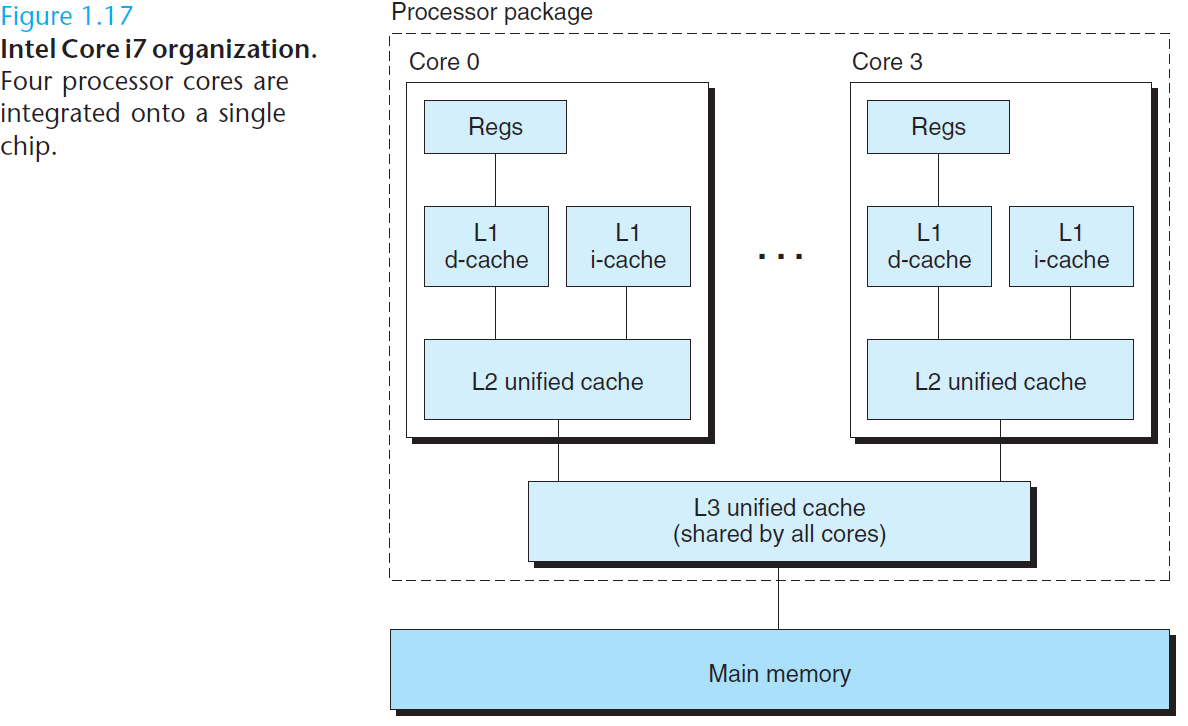
处理器读取并解释存放在主存里的二进制指令。因为计算机把大把的时间用于存储器、 I/O 设备和 CPU 寄存器之间复制数据,所以将系统中的存储设备划分层次结构— —CPU 寄存器在顶部,接着是多层的硬件高速缓存存储器、DRAM 主存和磁盘存储器。在层次模型中,位于更高层的存储设备比低层的存储设备要更快,单位比特开销也更高。层次结构中较高层次存储设备可以作为较低层次设备的高速缓存。通过理解和运用这种存储层次结构的知识,程序员可以优化 C 程序的性能。
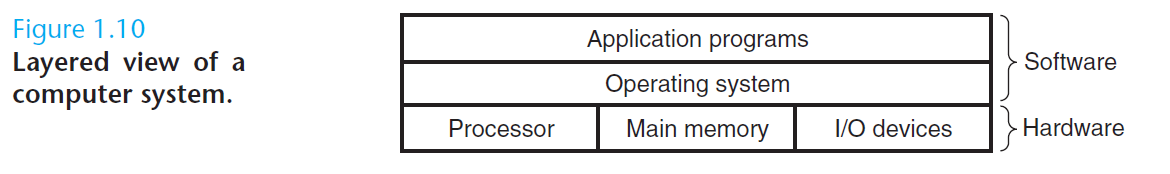
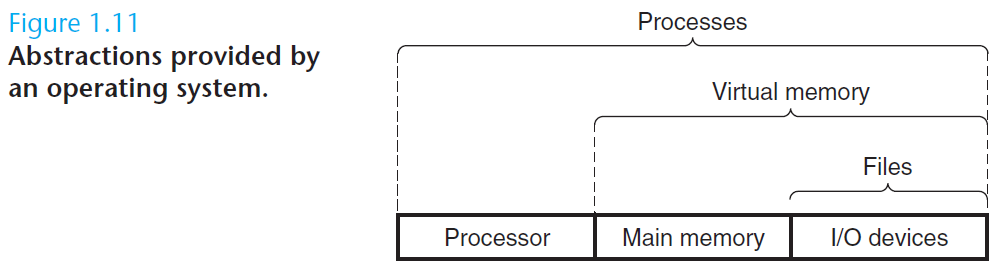
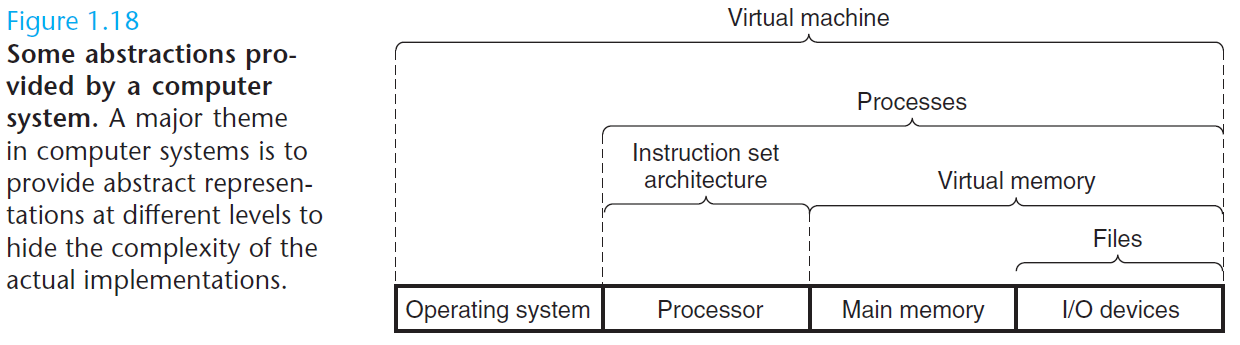
操作系统内核是应用程序和硬件之间的媒介。它提供三个基本的抽象:1)文件是对 I/O 设备的抽象;2)虚拟存储器是对主存和磁盘的抽象;3)进程是对处理器、主存和 I/O 设备的抽象。
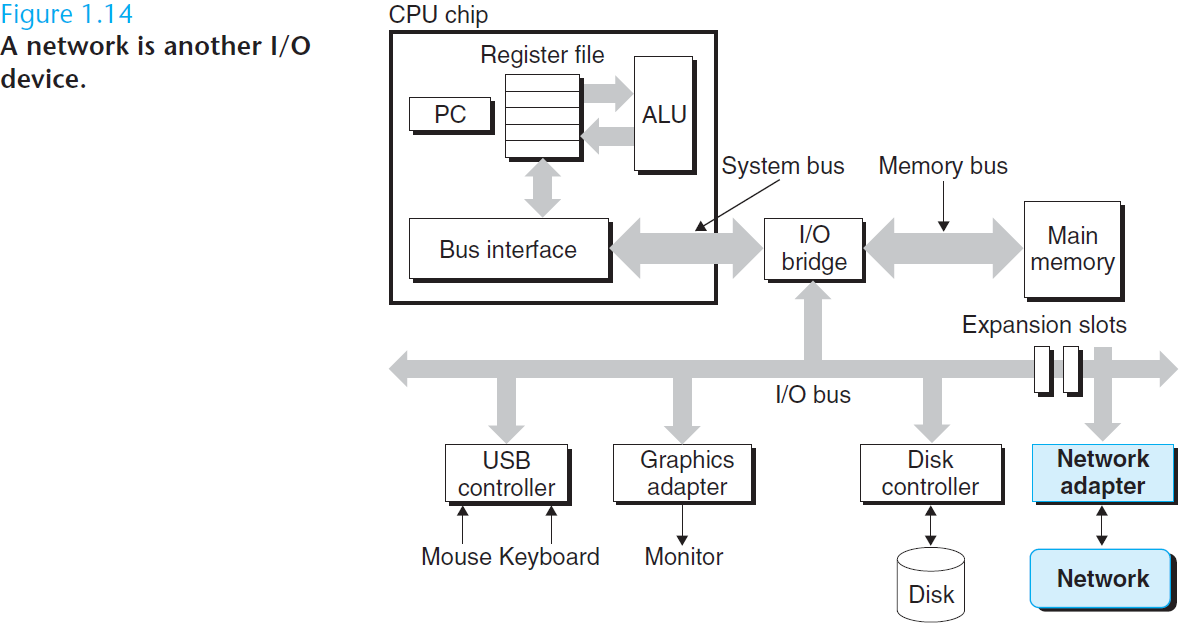
最后,网络提供了计算机系统之间的通信的手段。从特殊系统的角度来看,网络就是一种 I/O 设备。
A computer system consists of hardware and systems software that cooperate to run application programs. Information inside the computer is represented as groups of bits that are interpreted in different ways, depending on the context. Programs are translated by other programs into different forms, beginning as ASCII text and then translated by compilers and linkers into binary executable files.
Processors read and interpret binary instructions that are stored in main memory. Since computers spend most of their time copying data between memory, I/O devices, and the CPU registers, the storage devices in a system are arranged in a hierarchy, with the CPU registers at the top, followed by multiple levels of hardware cache memories, DRAM main memory, and disk storage. Storage devices that are higher in the hierarchy are faster and more costly per bit than those lower in the hierarchy. Storage devices that are higher in the hierarchy serve as caches for devices that are lower in the hierarchy. Programmers can optimize the performance of their C programs by understanding and exploiting the memory hierarchy.
The operating system kernel serves as an intermediary between the applica- tion and the hardware. It provides three fundamental abstractions: (1) Files are abstractions for I/O devices. (2) Virtual memory is an abstraction for both main memory and disks. (3) Processes are abstractions for the processor, main memory, and I/O devices.
Finally, networks provide ways for computer systems to communicate with one another. From the viewpoint of a particular system, the network is just another I/O device.